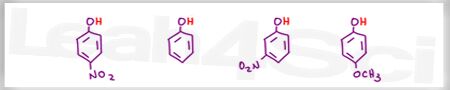
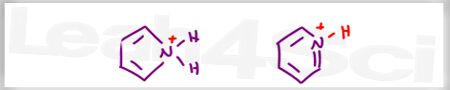
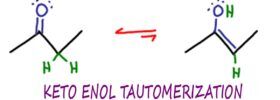
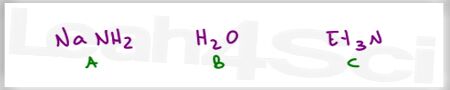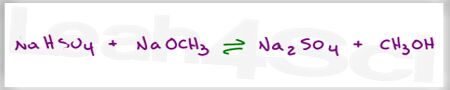Ready to test your knowledge of acids and bases with a few practice problems?
Ready to test your knowledge of acids and bases with a few practice problems?
This quiz is designed to follow my Acids and Bases tutorial video series. But I'm not looking to see if you simply ‘memorized' the concepts. The videos use simple examples to demonstrate concepts, these questions will test you at a slightly higher level.
So give it a shot, see how you do, then download the solutions at the end of the quiz.
Be sure to grab the Acid/Base Cheat Sheet to help you along.
Acid Base Practice Question 1
Which is the stronger acid?
Acid Base Practice Question 2
Rank the following ionic compounds in order of increasing base strength.
Acid Base Practice Question 3
Which of the following is the stronger base? (Not asking if it forms a stronger conjugate base)
Update: Although many organic textbooks state the pKa of water to be 15.7, the correct value for the pKa of water is 14.e
Acid Base Practice Question 4
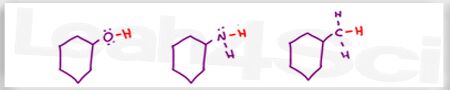
Which of the following is the stronger acid?
Acid Base Practice Question 5
Which of the following forms a stronger acid upon reacting with a proton?
Acid Base Practice Question 6
Rank the following in order of increasing base strength
Acid Base Practice Question 7
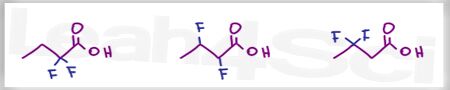
Rank the following in order of increasing acidity.
Acid Base Practice Question 8
Rank the following in order of increasing acidity.
Acid Base Practice Question 9
Label the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base in this reaction
Hint: Not sure which is which? Watch Acid/base video 1 for a quick refresher
Acid Base Practice Question 10
Label the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base in this reaction
Hint: Not sure which is which? Watch Acid/base video 1 for a quick refresher
Acid Base Practice Question 11
Rank the following in order of decreasing acidity
Acid Base Practice Question 12
Rank the following in order of increasing acidity
Acid Base Practice Question 13
Complete this acid base reaction and determine the position of equilibrium
Acid Base Practice Question 14
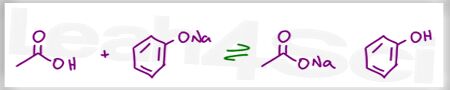
Complete this acid base reaction and determine the position of equilibrium
Acid Base Practice Question 15
Which of the following forms a weaker conjugate base?
Acid Base Practice Question 16
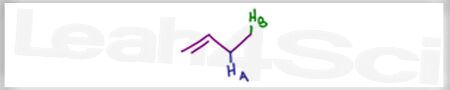
Which of the the labeled protons is more acidic, and why?
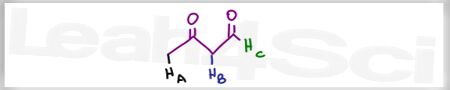
Acid Base Practice Question 17
Rank the labeled protons in order of increasing acidity.
Acid Base Practice Question 18
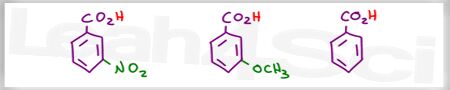
Which is the stronger acid?
Acid Base Practice Question 19
Which is the stronger acid and why?
Acid Base Practice Question 20
Which forms a weaker conjugate base and why?
Acid Base Bonus Practice Question 1
Rank the following in order of increasing acidity. Use resonance to back up your explanation.
Acid Base Bonus Practice Question 2
Which is the stronger acid and why?
Ready to see how you did?
Don't just right to t he solutions. Instead challenge yourself to try every question first.
Send Me The Solutions!