Alkene reactions are the core foundation to learning reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry. These are likely the first set of reaction mechanisms covered in your Orgo 1 course. But the concepts and foundations learned in these reactions will carry through to the rest of your organic chemistry 1 and 2 courses.
Alkene reactions are the core foundation to learning reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry. These are likely the first set of reaction mechanisms covered in your Orgo 1 course. But the concepts and foundations learned in these reactions will carry through to the rest of your organic chemistry 1 and 2 courses.
Below is my alkene reaction mechanism tutorial video series taking you through each reaction 1 at a time, focusing on the WHY and HOW for every step in every mechanism starting with an understanding of pi bond reactivity, role of nucleophile/electrophile and even covering hydride shifts and ring expansions.
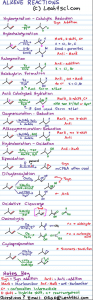
Included in this series:
- Naming Alkenes
- Introduction to Nucleophile, Electrophile and Pi Bond Reactivity
- Hydrohalogenation
- Halogenation
- Halohydrin Formation
- Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
- Hydride Shift vs Methyl Shift
- Ring Expansion via Hydride AND Methyl Shift
- Oxymercuration-Demercuration
- Alkoxymercuration-Demercuration
- Hydroboration Oxidation
- Alkene Epoxidation
- Ozonolysis
- Cyclopropanation
- Markovnikov v. Anti-Markovnikov
- Alkene Reaction Overview
Don't forget to download the Cheat Sheet + try the Alkenes Quiz after going through the series!
Video 1 – Naming Alkenes
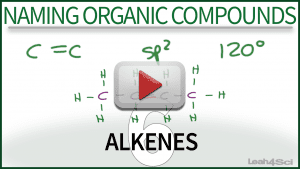 First, before we start looking at all of the various alkene reactions and mechanisms, do you remember how to name alkenes?
First, before we start looking at all of the various alkene reactions and mechanisms, do you remember how to name alkenes?
This video shows you how to name alkene molecules– from the simple to the more complex– using my puzzle piece approach to IUPAC naming of organic compounds.
It also includes a quick introduction to pi bonds and the hydrogen deficiency alkenes.
Video 2 – Introduction to Nucleophile/Electronphile and Pi Bond Reactivity
 Don't dismiss the intro video as ‘unimportant' this may very well be the most important video in this series.
Don't dismiss the intro video as ‘unimportant' this may very well be the most important video in this series.
In this video you'll get a proper view at the pi bond orientation and how this relates to alkene reactivity.
You'll also learn the true meaning of Nucleophile and Electrophile, including how to recognize them and why they react as they do.
And finally, this video takes you through a sample alkene reaction mechanism focusing on they WHY and HOW to ensure you understand the movement of electrons every step of the way.
Video 3 – Hydrohalogenation Reaction Mechanism
 The hydrohalogenation reaction is one in which the pi bond breaks adding a halogen to the more substituted carbon in keeping with Markovnikov's rule.
The hydrohalogenation reaction is one in which the pi bond breaks adding a halogen to the more substituted carbon in keeping with Markovnikov's rule.
This video takes you through the reaction and step by step mechanism for both a symmetrical starting alkene, and and asymmetrical starting alkene.
This mechanism typically involves hydrobromination and hydrochlorination in an inert solvent.
Carbocation rearrangements may be observed.
Video 4 – Halogenation of Alkenes Reaction Mechanism
 The alkene halogenation reaction is one in which the alkene pi bond breaks adding TWO halogen atoms to neighboring carbons. This occurs via a cyclic bromonium or chloronium intermediate.
The alkene halogenation reaction is one in which the alkene pi bond breaks adding TWO halogen atoms to neighboring carbons. This occurs via a cyclic bromonium or chloronium intermediate.
This video helps you understand the step by step reaction mechanism, from the halogen reactivity, bridge formation, and overall anti addition.
Do not confuse this with the alkene hydrohalogenation which only ads a single halogen along with a hydrogen atom.
This video demonstrates the mechanism for a symmetrical and asymmetrical starting molecule.
Video 5 – Halohydrin Formation
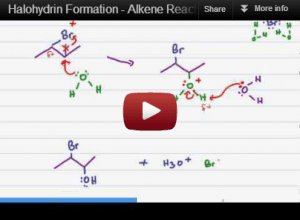 The halohydrin formation is an alkene reaction in which a halogen and an alcohol add to the broken pi bond.
The halohydrin formation is an alkene reaction in which a halogen and an alcohol add to the broken pi bond.
This reaction starts out just like the halogenation reaction, but since it takes place in a reactive solvent, you get a solvent molecule partaking in the reaction mechanism.
This video provides with a step by step breakdown of the mechanism and helps you understand WHY this reaction undergoes anti addition and still follows Markovnikov's rule.
 Learn The Backpack Trick
Learn The Backpack Trick
When students merely memorize, any change to a reaction may lead to panic. The backpack trick will help you figure out how to swap out atoms and groups to apply what you know to a new version of the reaction, specifically for oxygen containing reactions from acid catalyzed hydration and more.
Video 6 – Acid-Catalyzed Hydration Alcohol Formation
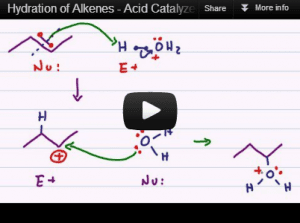 Acid catalyzed hydration is the reaction in which an alcohol is added to a pi bond following Markovnikov's rule.
Acid catalyzed hydration is the reaction in which an alcohol is added to a pi bond following Markovnikov's rule.
This tutorial video gives you a step by step logical breakdown of every step in the reaction mechanism to ensure you understand WHY each atom attacks as it does.
This reaction covers the role of solvent and catalyst in hydration reactions, and well as regioselectivity in accordance with Markovnikov's rule. Practice problems included.
For another step-by-step explanation, check out the article Acid Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes Reaction and Mechanism.
Video 7 – Hydride Shift vs Methyl Shift in Alkene Reactions
This video helps you understand the logic behind the most common types of carbocation rearrangements, along with specific patterns to look for when deciding between a hydride shift or methyl shift.
Video 8 – Ring Expansion Example with Hydride and Methyl Shift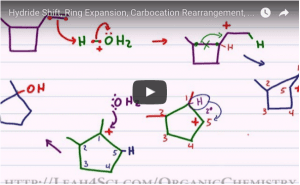
This video helps you understand the logic behind the carbocation rearrangement, along with specific patterns to look for when deciding between a hydride shift or methyl shift.
Video 9 – Oxymercuration & Demercuration
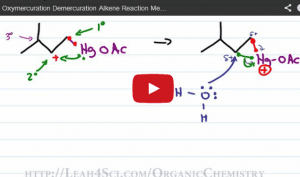 This video takes you through the step-by-step reaction mechanism for oxymercuration and helps you understand WHY there is no carbocation rearrangement.
This video takes you through the step-by-step reaction mechanism for oxymercuration and helps you understand WHY there is no carbocation rearrangement.
Video 10 – Alkoxymercuration & Demercuration
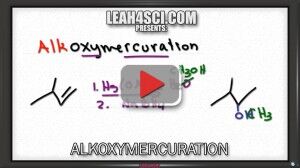 Alkoxymercuration-Demercuration Reduction is the alcohol version of the oxymercuration reaction.
Alkoxymercuration-Demercuration Reduction is the alcohol version of the oxymercuration reaction.
Just like its counterpart above, this reaction is regioselective in following Markovnikov's rule and will not exhibit a carbocation rearrangement.
The product of this reaction is an ether as detailed in this tutorial video.
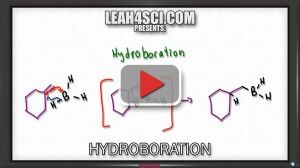
Video 11 – Hydroboration
The video below helps you understand the reactivity of Boron as well as the hydroboration and oxidation steps of the reaction mechanism.
Video 12 – Alkene Epoxidation
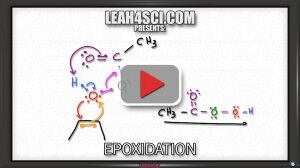 Understand peroxy acid (mCPBA and peroxyacetic acid). See a shortcut to quickly find the products, and finally the concerted cyclic mechanism to form the epoxide and carboxylic acid.
Understand peroxy acid (mCPBA and peroxyacetic acid). See a shortcut to quickly find the products, and finally the concerted cyclic mechanism to form the epoxide and carboxylic acid.
For another explanation of the reaction and mechanism, make sure to read my tutorial, Alkene Epoxidation Reaction and Mechanism with mCPBA.
Video 13 – Ozonolysis of Alkenes
The ozonolysis reaction of alkenes is one which breaks (or “lyses) both the sigma and pi bond of an alkene by reaction with a molecule of ozone. This video covers both the reductive and oxidative workups of the reaction.
It also provides a shortcut for quickly finding the products of an ozonolysis reaction, as well as the detailed step-by-step ozonolysis mechanism.
Video 14 – Cyclopropanation of Alkenes
This video covers the two common cyclopropanation reactions – the haloform and Simmons-Smith reactions. In both, an alkene reacts through a concerted reaction mechanism to form a cyclopropane in place of its pi bond. The first reaction proceeds through an unstable carbene intermediate, while the Simmons-Smith utilizes the more stable carbenoid.
Video 15 – Markovnikov v. Anti-Markovnikov

In so many of these alkene reactions, you might be asking yourself which addition product ACTUALLY forms? Or maybe, which one forms most often?
Asymmetrical alkenes can form two different addition products: one major and one minor. This video walks you through Markovnikov’s rule, including memorization shortcuts, to ensure you understand how to identify Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov addition products.
Video 16 – Alkene Reaction Overview
Time to review everything you’ve learned! This video reviews all 18 reactions covered on my alkene reaction cheat sheet and study guide. It also provides a quick overview of the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of products.
Ready to test your skills? Click HERE for my FREE Alkene Reactions Practice Quiz.
Or, for a quick review, download my free Alkene reactions study guide cheat sheet!