When it comes to MCAT prep, there are many resources available. Too many resources, in fact. There’s the recommended AAMC materials and many third party ones as well. Today, I want to discuss the AAMC resources specifically, including what they are, why you should use them, when to use them, and when to ABSOLUTELY AVOID […]
Complete Guide to Naming Ionic Compounds + Practice Questions
When it comes to naming ionic compounds, It’s not as straightforward as with IUPAC Nomenclature. You have to consider: Is it a metal, nonmetal, or a transition/post-transition metal with a varying charge? Are there multiple atoms in this ion, like polyatomic ions? Is the compound balanced and neutral? That’s exactly what you’ll learn in this […]
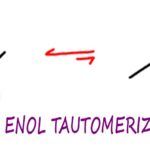
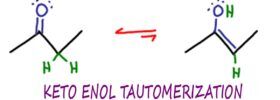
Keto Enol Tautomerization Reaction and Mechanism
Keto Enol Tautomerization or KET, is an organic chemistry reaction in which ketone and enol molecules can isomerize or interconvert, typically in an acid or base catalyzed reaction.
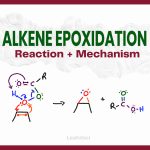
Alkene Epoxidation Reaction and Mechanism with mCPBA
Reaction Overview: Alkene epoxidation is a reaction in which the pi bond of an alkene breaks and both of the former sp2 carbon atoms bind to the same oxygen atom, forming a 3-membered ring known as an epoxide. This reaction requires a peroxycarboxylic acid, such as m-CPBA. Epoxidation happens via a concerted reaction mechanism and […]
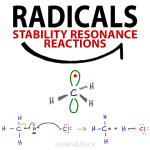
Free Radicals Organic Chemistry – Reactions Resonance Stability Hybridization
A radical, or free radical, refers to an atom or molecule with a single unpaired electron. This concept differs from 99% of organic chemistry which deals with the movements and reactions of electron pairs. Before we dive into free radical reactions, let’s take a step back to understand the nature and chemistry of these mysterious […]
How to Tackle Organic Chemistry Synthesis Questions
Organic chemistry may cover many concepts and topics, but it’s all about the reactions and mechanisms. It’s not so scary at first, think about the simple acid/base deprotonation, an alkene reaction here, another there. Before you know it, you’re drowning in dozens upon dozens of reactions! You’re asked to ‘memorize’ each one, to know what every […]
Math Bootcamp
Math Bootcamp
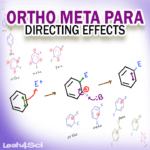
Ortho Meta Para Directing Effects in EAS Reactions
Ortho, Meta and Para refer to the 1-2, 1-3, and 1-4 relationships between benzene substituents. In Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reactions, O/M/P directing effects help us figure out where to place the incoming electrophile. Electron Donating Groups activate the ring for ortho and para addition. Electron Withdrawing Groups deactivate the ring for meta addition. Halogens are the one exception.
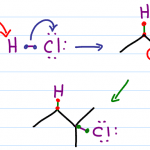
Hydrohalogenation Of Alkenes – Reaction Mechanism
Reaction Overview: The hydrohalogenation of alkenes involves breaking a carbon to carbon double bond, followed by the electrophilic addition of a hydrogen atom and halogen. The halide will add to the more substituted carbon following Markovnikov’s rule. The product is a haloalkane also called an alkyl halide. Summary of Hydrohalogenation Mechanism Nucleophilic pi bond reaches […]
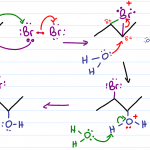
Halohydrin Formation – Alkene Reaction Mechanism
Reaction Overview: The Halohydrin formation reaction involves breaking a pi bond and creating a halohydrin in its place. Halo = halogen and Hydrin = OH. This reaction takes place in water and yields an anti-addition reaction which follows Markovnikov’s rule. Reaction Summary Nucleophilic pi bond attacks halogen molecule, pi bond breaks in the process Halogen lone […]