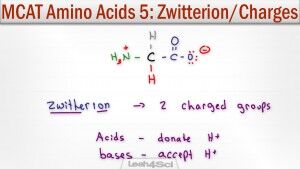
 Amino acids exist as zwitterions at physiological pH. A zwitterion by definition is a molecule with 2 (zwitter) ions, one positive and one negative for a net zero charge.
Amino acids exist as zwitterions at physiological pH. A zwitterion by definition is a molecule with 2 (zwitter) ions, one positive and one negative for a net zero charge.
This video shows you how to quickly calculate amino acid charge at any given pH by helping you recognize when a given side chain is protonated or deprotonated.
(Watch on YouTube: Zwitterion and Amino Acid Charge. Click cc on the bottom right for video transcript)
< — Watch Previous Video: Stereochemistry of Amino Acids RS to DL
— >Watch Next Video: Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids with MCAT shortcut
This is video 5 in the Amino Acids Series. Click for complete series + Practice Quiz and Cheat Sheet
Have you grabbed the FREE Printable Cheat Sheet to follow along? CLICK HERE


Leah, is this the best way to calculate the charge of an amino acid? In my orgo review book, it also states you can calculate charge from the isoelectric point. Using the pKa method, then all amino acids, except for the acid and base ones, would be neutral at physiological pH. However, using the isoelectric point method (in my review book), it states if pH is greater than pI then the amino acid would be in the basic forms which would be negatively charged.
For example, glycine using pka method would be neutral at physiological pH. However, using pI method, glycine has a pI of approximately 6, then at physiological pH, it should be negatively charged since pH is greater than pI. Can you please tell me what method is best, and whether my intuition that only the charged amino acids are charged at physiological pH is true or not?
This is amazing thank you so much I literally COULD NOT understand this concept before your video and now it makes perfect sense.Thank you!